Galvanised sheets
Characteristics of the material
The galvanised sheet is a layered material where the optimum properties of steel (see the physical parameters) are combined with the protective effect of a zinc layer against corrosion. Galvanised steel is produced by a continuous process. The cold-rolled steel sheet as the basic material is continuously cleaned, annealed and galvanised in a melted zinc bath. The thickness of the double-side zinc coating is adjusted by application of electrolytic jet thinning.
Surface treatment
The weight of the zinc layer in galvanised sheets is in the range of 60-450 g/m2, always double-sided. The weight is labelled in the name of the material – for example, DX51D + Z275 is a sheet with DX51D steel (see the physical parameters) and the zinc coating weight of 275 g/m2. The thickness of the zinc layer is in the range of 10-25 µm. During zinc solidification a typical surface structure, the so-called zinc flowers, is created. The size of the zinc flowers can be managed by controlled interference in the zinc layer or by the chemical composition of the zinc bath. In this way, it is possible to achieve a surface without zinc flowers or surfaces with various zinc flowers. Normal zinc flowers are achieved by no interference in solidification of the zinc coating.
Small zinc flowers
Deliberate interference in the zinc layer during the solidification process results in a large amount of small zinc flowers. The surface has a uniform appearance.
Additional rolling
This additional modification smooths the zinc flowers in the top layer. The result is a uniform grey matt surface. Another type of surface treatment is a plastic layer. As galvanised steel sheets with additional plastic layers are the most frequently used material in the DEKMETAL system, their properties and parameters are described in the separate Organic coated sheets section.
Processing
Joining
It is possible to use classic joining methods such as riveting, bolting, fluting, flanging, etc., because these methods do not compromise the protective effect of zinc against corrosion. When connecting with other metals, it is necessary to bear in mind that contact corrosion occurs with the creation of an electrochemical cell.
Welding
It is possible to use standard fusion welding for the welding of galvanised sheets. However, it can result in a breach of the zinc coating in the welding area. It is thus recommended to apply a zinc paint as additional protection. Resistance welding is moreover recommended because the anti-corrosive protective layer remains largely intact.
Life and corrosion
Protective parameters of the zinc layer
After a short time, a strongly adhering grey layer of oxidising zinc products – the zinc patina – appears on the zinc surface. On the external surface, this coating is permanently degraded and at the same time replenished from the zinc underneath. The protective period thus depends on the thickness of the zinc layer and the parameters of the external environment.
White rust
White rust is an undesirable bulky white and badly adhering product of zinc corrosion. It can occur due to bad transport or storage conditions, for example in great temperature differences. Condensed water penetrates deep into the stack of the sheets or rolls as the result of a capillary effect. Simultaneously a zinc patina develops, but due to insufficient air supply, the water cannot evaporate. In this way, this patina layer is very quickly degraded and the white rust develops. Smaller amounts of the white rust have a low impact on anti-corrosive protection. However, its noticeable appearance makes it undesirable. To avoid damage by white rust during transport and storage, the galvanised steel strip can be passivated by chromatising or delivered in an oiled condition.
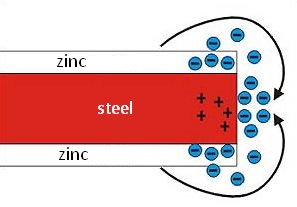
Cathodic protection
Cathodic protection is a protective mechanism of the zinc layer, which is based on the zinc ions' ability to move to the damaged part of the steel sheet. A galvanic cell is created between two various metals by the action of rainwater, condensate and other electrolytes. This results in a difference in the voltage and the less noble metal (zinc) is transferred into the solution as an anode. It means that because of its normal potential, zinc behaves like the consumed anode, thus protecting the basic material.
Physical parameters
Regarding requirements for using steel sheets in the DEKMETAL systems, the applicable standards and two types of steel are used for description and physical parameters. Mild steels for cold forming – EN 10 327 standard.